What are the components of Java Architecture?
Java Architecture combines the process of compilation and interpretation. It explains the various processes involved whilst formulating a Java program. Before I begin with the topic let me introduce you with the agenda for this article.
Below mentioned pointers will be our topics of discussion:
Let us begin by understanding what exactly is Java Architecture?
What is Java Architecture?
Here, I will explain you the java architecture in simple steps.
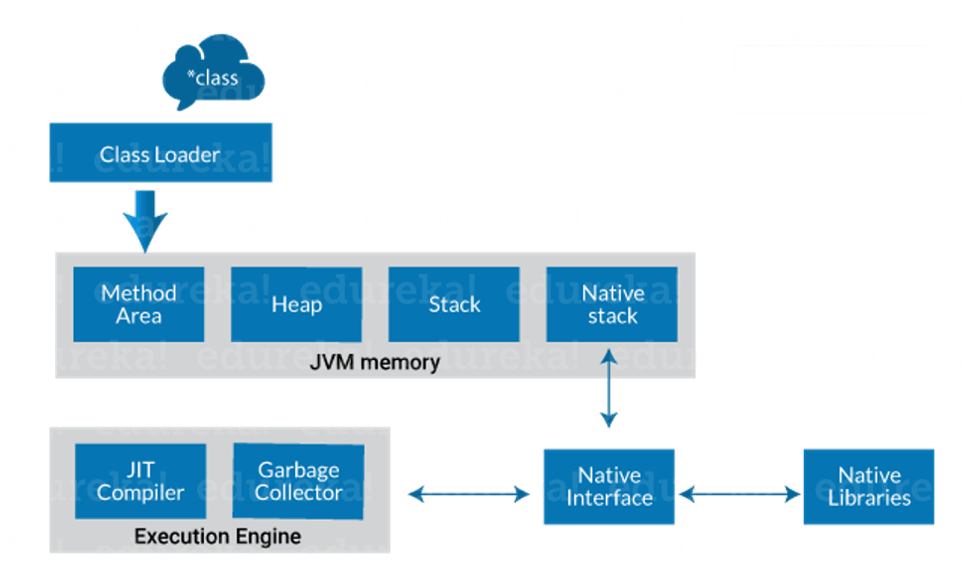
This diagram illustrates the internal working of a Java code, or precisely, Java Architecture!
Components of Java Architecture
There are three main components of Java language: JVM, JRE, and JDK.
Java Virtual Machine, Java Runtime Environment and Java Development Kit respectively.
Let me elaborate each one of them one by one:
Java Virtual Machine:
Ever heard about WORA? (Write once Run Anywhere).? Well, Java applications are called WORA because of their ability to run a code on any platform. This is done only because of JVM. The JVM is a Java platform component that provides an environment for executing Java programs. JVM interprets the bytecode into machine code which is executed in the machine in which the Java program runs.
Explanation:
Class Loader: Class loader is a subsystem of JVM. It is used to load class files. Whenever we run the java program, class loader loads it first.
Class method area: It is one of the Data Area in JVM, in which Class data will be stored. Static Variables, Static Blocks, Static Methods, Instance Methods are stored in this area.
Heap: A heap is created when the JVM starts up. It may increase or decrease in size while the application runs.
Stack: JVM stack is known as a thread stack. It is a data area in the JVM memory which is created for a single execution thread. The JVM stack of a thread is used by the thread to store various elements i.e.; local variables, partial results, and data for calling method and returns.
Native stack: It subsumes all the native methods used in your application.
Execution Engine:
JIT compiler: The Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler is a part of the runtime environment. It helps in improving the performance of Java applications by compiling bytecodes to machine code at run time. The JIT compiler is enabled by default. When a method is compiled, the JVM calls the compiled code of that method directly. The JIT compiler compiles the bytecode of that method into machine code, compiling it “just in time” to run.
Garbage collector: As the name explains that Garbage Collector means to collect the unused material. Well, in JVM this work is done by Garbage collection. It tracks each and every object available in the JVM heap space and removes unwanted ones. Garbage collector works in two simple steps known as Mark and Sweep:
Java Runtime Environment:
The JRE software builds a runtime environment in which Java programs can be executed. The JRE is the on-disk system that takes your Java code, combines it with the needed libraries, and starts the JVM to execute it. The JRE contains libraries and software needed by your Java programs to run. JRE is a part of JDK (which we will study later) but can be downloaded separately.
Java Development Kit:
The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a software development environment used to develop Java applications and applets. It contains JRE and several development tools, an interpreter/loader (java), a compiler (javac), an archiver (jar), a documentation generator (javadoc) accompanied with another tool.