Unlocking the Mysteries of Matter: A Glimpse into Density Functional Theory
Archishman Gupta
Aspiring Physicist | Computational Material Science & Nanotechnology | IIT BHU
In the realm of computational chemistry and physics, Density Functional Theory (DFT) stands as a cornerstone for understanding and predicting the behaviour of matter at the atomic and molecular levels. As industries and research fields strive for more precise and efficient tools, DFT has emerged as an invaluable method bridging theory and practical applications.
Read : https://tinyurl.com/2rr6ufc8
What Is Density Functional Theory?
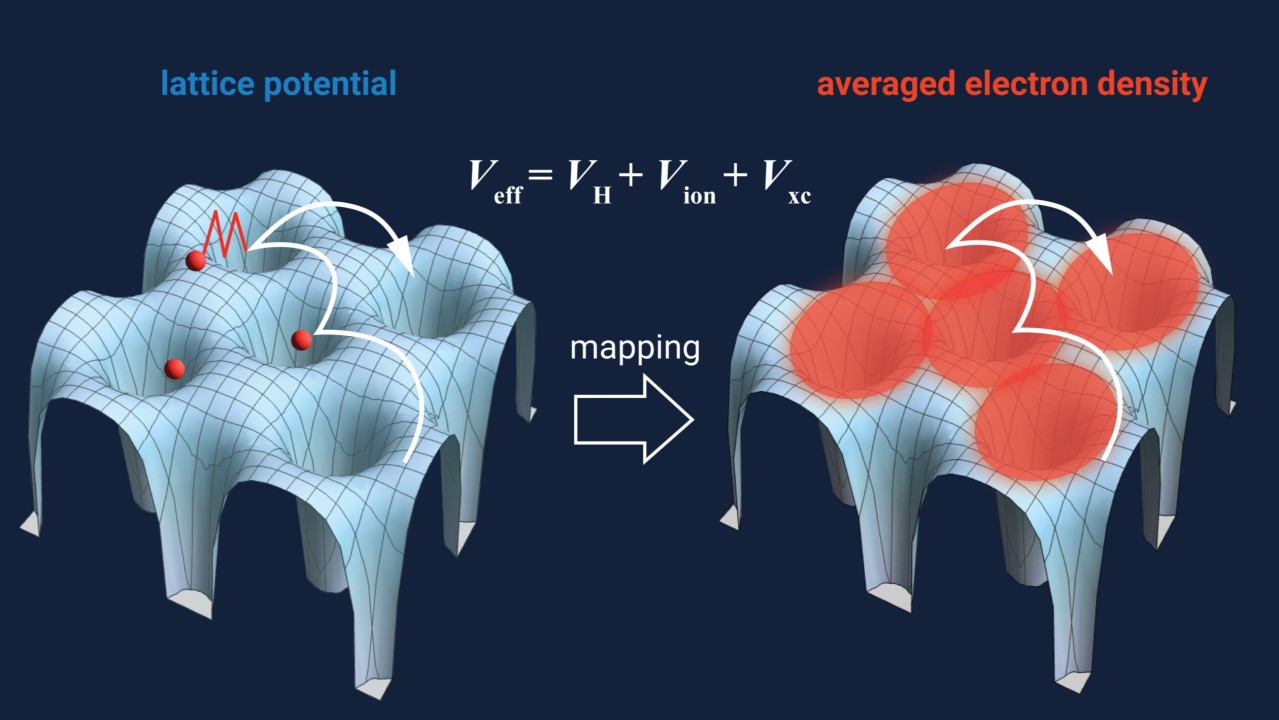
At its core, Density Functional Theory is a quantum mechanical modeling method used to investigate the electronic structure of many-body systems, primarily atoms, molecules, and condensed matter. Unlike traditional quantum chemistry methods that scale poorly with system size, DFT leverages the electron density—a simpler and more computationally efficient parameter—as the primary variable instead of the many-body wave function.
Introduced by Hohenberg and Kohn in 1964, and expanded through Kohn and Sham’s formulation in 1965, DFT has undergone significant refinement, becoming a standard tool for physicists, chemists, and material scientists.
Why Does DFT Matter?
DFT is celebrated for its ability to address complex systems with a balance of accuracy and computational efficiency. Its applications span diverse domains:
1. Materials Science: DFT predicts the properties of new materials, from semiconductors to superconductors, without needing extensive physical experimentation.
2. Catalysis: It helps design catalysts by modeling surface reactions and understanding energy barriers.
3. Drug Discovery: DFT elucidates molecular interactions critical for developing therapeutic agents.
4. Energy Storage: Researchers utilize DFT to explore battery materials and optimize renewable energy technologies.
Recent Advances in DFT
While DFT has revolutionized many fields, challenges like the accurate treatment of dispersion forces and strongly correlated systems remain. Recent advancements include:
领英推荐
? Hybrid Functionals: These incorporate a mix of exact exchange from Hartree-Fock theory and conventional DFT approximations, improving accuracy for many systems.
? Machine Learning Integration: AI models are now aiding functional development, speeding up calculations and enhancing predictive power.
? DFT in Big Data: By leveraging databases of computed materials properties, DFT is driving high-throughput screening for materials innovation.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its strengths, DFT is not without limitations. Accuracy depends heavily on the choice of exchange-correlation functionals, and approximations can lead to significant errors in specific scenarios. For example, systems with strongly localized electrons, such as transition metal oxides, often require advanced treatments like DFT+U or beyond-DFT methods.
Looking Ahead
The future of Density Functional Theory lies in interdisciplinary innovation. As computational resources grow and algorithms evolve, DFT will continue to shape the landscape of scientific discovery, offering deeper insights into the mysteries of the quantum world.
Final Thoughts
DFT is a testament to how theoretical advancements can profoundly impact practical applications. From enabling the design of groundbreaking materials to advancing fundamental science, Density Functional Theory is a shining example of how we can decode the universe’s building blocks.
For professionals and researchers eager to harness the potential of DFT, the message is clear: now is the time to embrace this transformative tool and be part of the next wave of innovation.