A Unified Deep Learning Anomaly Detection Approach for Smart Grid: Check our latest work in the IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management!
Panagiotis Sarigiannidis
Director of ITHACA Lab | Co-founder of MetaMind Innovations P.C. | Full Professor University of Western Macedonia
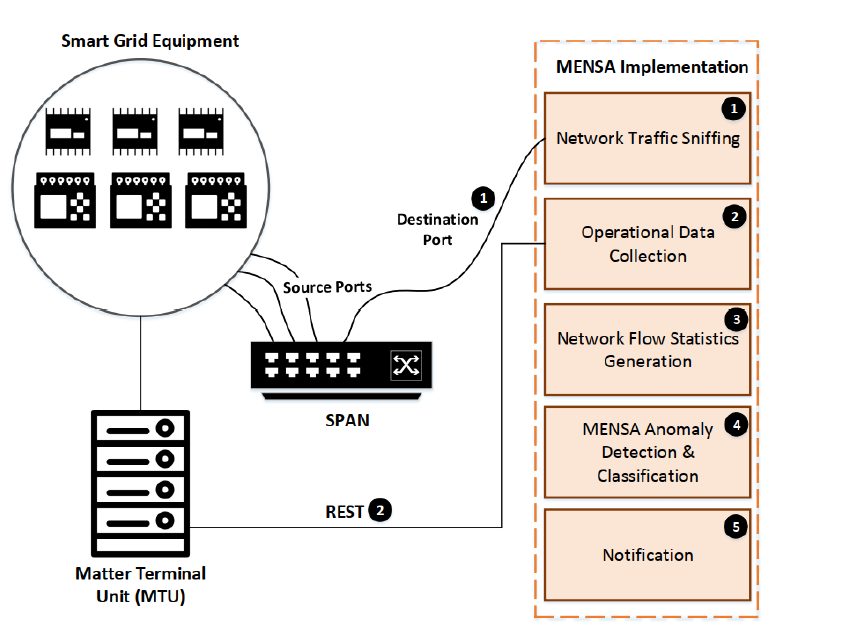
Our latest work, published in IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management (available in ResearchGate), presents an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) for Smart Grid (SG) environments, where the Modbus/Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3) protocols are involved.
The so-called MENSA: anoMaly dEtection aNd claSsificAtion adopts a novel Autoencoder-Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) architecture for a) detecting operational anomalies and b) classifying Modbus/TCP and DNP3 cyberattacks.
MENSA combines Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) in a common architecture by taking into account the adversarial loss and the reconstruction difference. The proposed IDS is assessed in 4 SG evaluation environments, namely a) SG lab, b) substation, c) hydropower plant, and d) power plant.
MENSA excels in solving successfully an outlier detection (i.e., anomaly detection) problem as well as a challenging multiclass classification problem consisting of 14 classes (13 Modbus/TCP cyberattacks and normal instances).
Also, MENSA is able to discriminate five cyberattacks against DNP3. The evaluation results demonstrate the efficiency of MENSA compared to other Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) methods in terms of Accuracy, False Positive Rate (FPR), True Positive Rate (TPR) and the F1 score
MENSA is an output of the H2020 DS-07-2017, SPEAR: Secure and PrivatE smArt gRid project, which is coordinated by the University of Western Macedonia.
Proud to share our research work with you :)