?? Understanding the Basics of Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) ??
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) might sound like a complex topic, but it’s crucial in our modern, technology-driven world. From smartphones ?? to medical devices ??, and even your electric car ??, ensuring these devices work without interference is essential. Whether you're an engineer, a tech enthusiast, or just curious, this guide will help you grasp the basics of EMC in a simple and engaging way. Let’s dive in! ??
DOWNLOAD PDF: CONTROL OF MECHATRONIC SYSTEM
?? What is EMC?
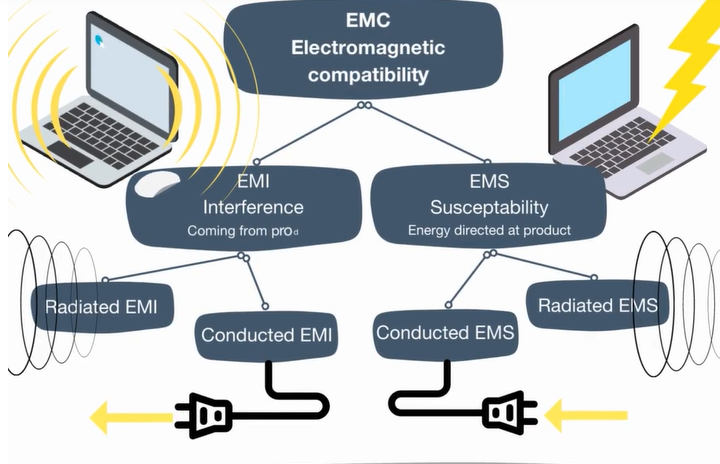
EMC stands for Electromagnetic Compatibility, a field focused on ensuring that electrical and electronic devices can operate together without interference. It involves two main components:
Imagine listening to the radio ?? while charging your phone. Without proper EMC design, the charger could interfere, causing static noise. EMC ensures harmony among devices.
DOWNLOAD PDF: MECHATRONICS AND MEASUREMENT SYSTEM
? Why is EMC Important?
Here’s why EMC matters in our everyday lives:
领英推荐
DOWNLOAD PDF: ROBOTICS AND MECHATRONICS FOR AGRICULTURE
?? Key Concepts in EMC
??? Common Techniques for EMC Compliance
?? EMC in Industry Applications
?? Challenges in EMC
The growing complexity of modern technology poses unique challenges for EMC:
?? Future Trends in EMC
?? Takeaway Tips
OK Bo?tjan Dolin?ek
Experienced Administration and Supply Clerk with Attention to Detail
3 个月Very informative
Mechanical engineer | Project Manager ?? I help big and small businesses automate their manual tasks?? handle projects??, break down tasks and help track progress ?efficiently while ensuring cost is efficiently managed.
3 个月Very informativg
Great perspective