?? Understanding the ABCs of Cloud Computing: Exploring IaaS, TaaS, and SaaS
?? What do you know about Cloud? ??
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals consume and manage IT resources. At its core, the cloud refers to a network of remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process data, applications, and services. It offers a flexible and scalable alternative to traditional on-premises infrastructure, enabling organizations to access computing resources on-demand and pay only for what they use.
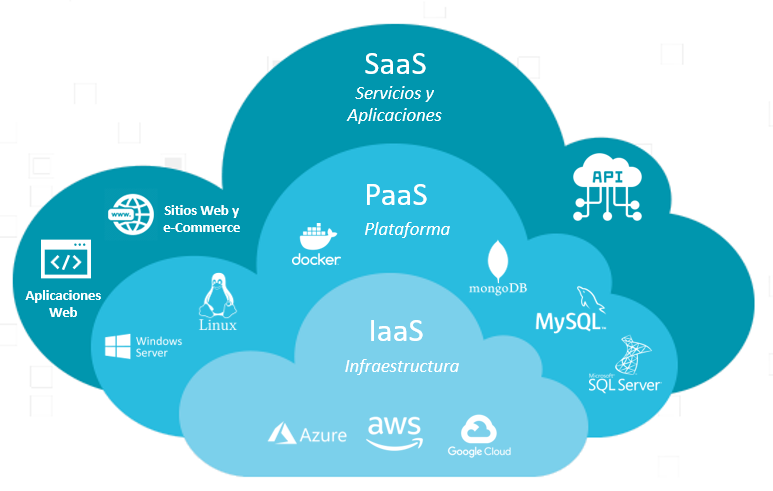
Cloud computing encompasses various service models, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). These models provide users with different levels of control and management over their IT environments, catering to diverse business requirements and preferences.
?? Defining TaaS, IaaS, and SaaS ??
In the dynamic landscape of information technology (IT), testing professionals are continually challenged to adapt to new models and methodologies. Three prominent models that have reshaped the way testing is approached are Testing as a Service (TaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). These models are intricately connected with the cloud, leveraging its capabilities to streamline testing processes and enhance efficiency.
???????? Testing as a Service (TaaS):
TaaS revolutionizes the testing paradigm by offering testing services as an on-demand service. Instead of relying solely on internal testing resources and infrastructure, organizations can outsource their testing needs to TaaS providers. TaaS encompasses the provision of testing environments, tools, and skilled testing professionals. This model allows companies to scale testing efforts dynamically, improve testing efficiency, and reduce costs associated with maintaining in-house testing infrastructure.
???????Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, enabling organizations to rent infrastructure components such as servers, storage, and networking on a pay-per-use basis. Testing teams can leverage IaaS to quickly provision and configure test environments, access scalable computing power, and reduce the overhead of managing physical infrastructure. IaaS empowers testers to focus on testing activities rather than infrastructure maintenance, facilitating agility and cost-effectiveness in testing processes.
??????Software as a Service (SaaS):
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for users to install, maintain, and upgrade software locally. From a testing perspective, SaaS applications present unique challenges and opportunities. Testers must adapt their testing strategies to address aspects such as data security, interoperability, and integration with other SaaS solutions. Testing SaaS applications requires a comprehensive understanding of the underlying architecture, data flows, and user interfaces to ensure optimal performance and user experience.
?? Comparative Analysis: TaaS, IaaS, and SaaS ??
??Examples ??
1??Testing as a Service (TaaS):
Example 1: A software development company opts for TaaS to conduct comprehensive regression testing for their latest software release. They engage a TaaS provider to execute test cases across multiple platforms and devices, leveraging the provider's testing expertise and infrastructure.
Example 2: A startup specializing in mobile app development partners with a TaaS vendor to perform load testing for their application. The TaaS provider simulates thousands of concurrent users to evaluate the app's performance under various traffic conditions.
2?? Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
Example 1: An e-commerce platform utilizes IaaS to dynamically scale its web servers during peak shopping seasons. By leveraging IaaS, the platform can accommodate increased user traffic without investing in additional physical hardware.
Example 2: A data analytics firm leverages IaaS to deploy virtual machine instances with specialized computing capabilities. They adjust resource allocations as per project requirements, optimizing cost and performance for data processing tasks.
领英推荐
3??Software as a Service (SaaS):
Example 1: A business adopts a SaaS-based customer relationship management (CRM) system to streamline sales and marketing processes. Employees access the CRM application via web browsers, eliminating the need for on-premises software installation.
Example 2: An educational institution subscribes to a SaaS learning management system (LMS) to deliver online courses to students. The LMS platform provides instructors with tools for course creation, student engagement, and performance tracking, all hosted and managed by the SaaS provider.
By examining the nuances of Testing as a Service (TaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) models, functional testers gain insights into the diverse approaches to IT service delivery. Understanding the specific characteristics, benefits, and examples of each model empowers testers to make informed decisions, optimize testing strategies, and contribute effectively to the quality assurance process in modern IT environments.
??Brief overview of testing in Testing as a Service (TaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS):
1??Testing as a Service (TaaS):
?? TaaS offers testing services as an on-demand solution, typically leveraging cloud-based resources.
?? Testing teams can access a variety of testing tools and environments without maintaining their own infrastructure.
?? TaaS providers offer services such as test automation, performance testing, and security testing.
?? Testing in TaaS focuses on ensuring the quality and reliability of software applications across different platforms and devices.
2??Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
?? IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, allowing organizations to rent infrastructure components.
?? Testing teams can dynamically provision and configure testing environments on the cloud, scaling resources as needed.
?? IaaS enables testers to set up test environments, deploy applications, and conduct various types of testing, including functional testing and load testing.
?? Testing in IaaS emphasizes resource optimization, scalability, and cost-effectiveness in managing testing infrastructure.
3??Software as a Service (SaaS):
?? SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance.
?? Testing SaaS applications involves validating functionality, performance, and security aspects within the SaaS environment.
?? Testers focus on ensuring seamless integration, data security, and user experience across different SaaS platforms.
?? Testing in SaaS emphasizes understanding the underlying architecture and user workflows to deliver high-quality software solutions.
In summary, testing in TaaS, IaaS, and SaaS environments requires adaptation to the specific characteristics and challenges of each model, leveraging cloud-based resources and services to ensure the quality and reliability of software applications.
AVP Technology Solutions Sales | Specializing in Cloud Solutions, DAAS Resource Augmentation | Enabling Business to achieve IT Efficiency and Growth .
4 个月Great insights! This is especially relevant to us at PrimeCrown Technologies, where we focus on cloud infrastructure/innovative tech solutions]. Thanks for sharing this valuable information!???
Helping Tech Founders Go To Market (Growth, Leadership, Sanity)
1 年Sounds like a comprehensive guide to Cloud Computing! Looking forward to exploring the ABCs of IaaS, TaaS, and SaaS. ????
Snowflake |Top Customer Success Professional | Data Architect & Evangelist | Apple & Snowflake Veteran | Performance Tuning Expert | Engineering Leadership | Business Strategist & Entrepreneur| Community Leader -Speaker
1 年Exciting topic! Can't wait to learn more about Cloud Computing. ????