Topology-Aware Routing in Kubernetes: Improved Efficiency and Lower Costs!
Sandip Das
AWS Container Hero | Founder @ Good Cloud Development | Cloud & DevOps Architect for Startups | Kubernetes Specialist | SRE, Platform Engineering & MLOps Enthusiast | Educator | Mentor
Topology-aware routing is a powerful feature in Kubernetes that optimizes internal traffic flows, reduces latency, and minimizes inter-zone data transfer costs.
What is Topology-Aware Routing?
Topology-aware routing (formerly known as topology-aware hints) is a feature that allows Kubernetes services to route traffic based on the topology of the cluster, such as the node’s physical location (e.g., which Availability Zone it belongs to). The goal is to keep traffic within a local zone whenever possible, which minimizes cross-zone traffic costs and latency. This is particularly beneficial for high-availability applications where reducing cost and improving performance are key.
How Topology-Aware Routing Works
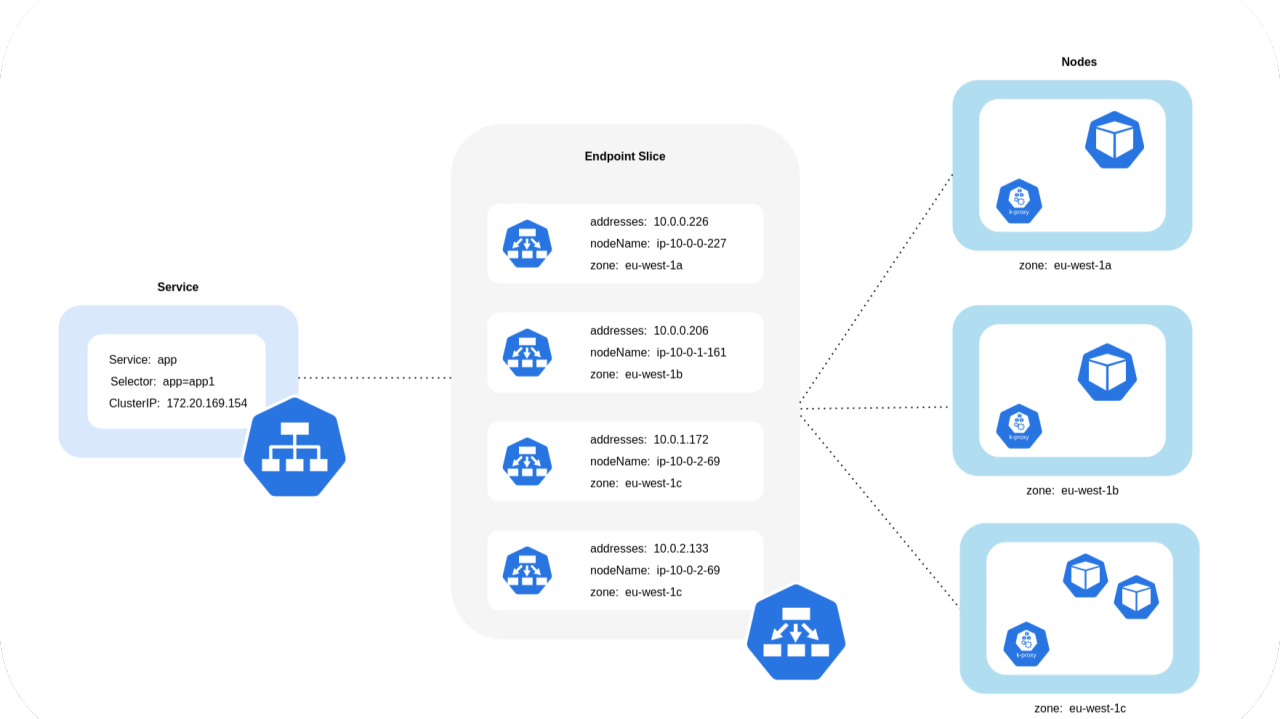
When a Kubernetes Service is created, multiple EndpointSlices are automatically created. These EndpointSlices hold metadata about endpoints, such as IP addresses and the zones they belong to. Topology-aware routing works by assigning hints to these endpoints, which are then used by kube-proxy to make intelligent routing decisions.
In practical terms, here’s how the routing happens:
This approach is particularly effective for reducing cross-zone data transfer charges, which can accumulate significantly if workloads are distributed across multiple zones.
Configuration Example
To configure a Kubernetes Service with topology-aware routing, you can add an annotation to your Service manifest as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: api-service
namespace: backend
annotations:
service.kubernetes.io/topology-mode: Auto
spec:
selector:
app: api
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
The annotation service.kubernetes.io/topology-mode: Auto enables the Kubernetes EndpointSlice controller to apply hints based on the node topology. This setting ensures that traffic is primarily routed to endpoints within the same zone.
领英推荐
Key Benefits
Best Practices
Considerations and Limitations
Use Cases in Production Environments
Topology-aware routing is especially useful in scenarios where cross-zone data transfer is frequent and costly. Some typical use cases include:
Special note
How to Handle Scaling in Topology-Aware Routing Scenario?
Using Topology Spread Constraints:
We can use Topology Spread Constraints in Kubernetes to distribute pods evenly across different topology domains, such as zones or nodes, to ensure reliability and availability. Here's how:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: api
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: api
spec:
topologySpreadConstraints:
- maxSkew: 1
topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone
whenUnsatisfiable: ScheduleAnyway
labelSelector:
matchLabels:
app: api
containers:
- name: api-container
image: api-image
Conclusion
Topology-aware routing is a valuable feature for optimizing cost and performance in Kubernetes clusters, particularly in AWS EKS environments. By using this feature effectively, you can ensure that your applications are not only highly available but also efficient in their network usage, reducing costs and improving performance.
For Kubernetes administrators managing multi-zone clusters, enabling topology-aware routing can be a key step towards more efficient cloud resource usage.
DevOps Engineer @ Pipeline Co., Ltd | AWS Community Builder | PeopleCert DevOps Ambassadors
1 个月Most needed. Thanks
Experienced Amazon FBA VA | Looking for Roles in Product Research, PPC, and E-commerce Growth
1 个月Important