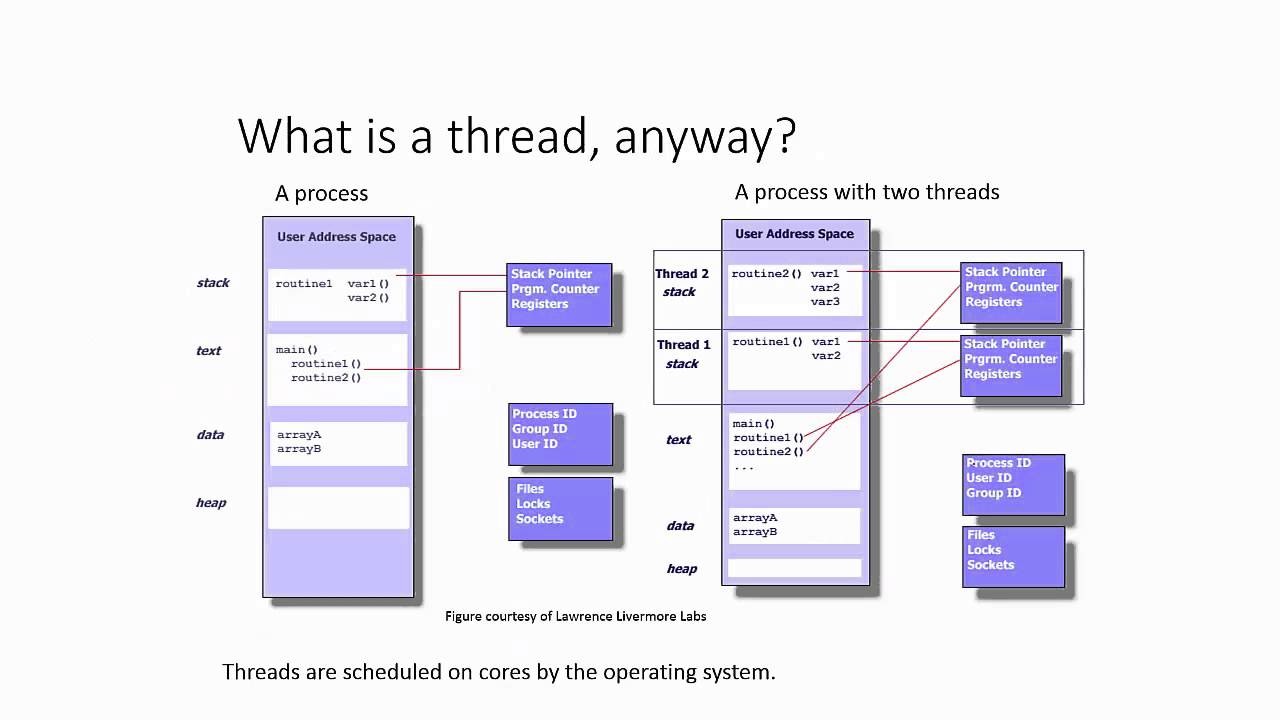
Threads in React Native
React Native uses a single JavaScript thread to execute the application code, which is the main thread.
JavaScript, as a single-threaded language, only has one thread of execution, also known as the "main thread". This means that JavaScript code is executed in a single, sequential order, one statement at a time, and can only do one thing at a time.
However, JavaScript also provides mechanisms for asynchronous programming, such as callbacks, promises, and async/await, which allow developers to write code that can execute in parallel with the main thread. These mechanisms use the browser's or the runtime's internal thread pool to execute code in the background, while the main thread continues to execute other code.
For example, when making an HTTP request using JavaScript, the browser uses a separate thread to send the request and receive the response, while the main thread continues to execute other code. Once the response is received, the browser uses a callback or promise to notify the main thread that the response is ready and can be processed.
So while JavaScript itself only has one thread of execution, it can still take advantage of other threads provided by the browser or the runtime to execute code in the background and improve performance.
However, React Native also provides APIs that allow developers to create additional threads to offload work from the main thread and improve performance. These additional threads can be created using the Worker API or other third-party libraries.
It's important to note that creating too many threads can actually have a negative impact on the performance of the application, as each thread comes with its own overhead and can compete for resources with other threads. Therefore, it's important to use threads judiciously and only when necessary to improve the performance of specific tasks.
React Native uses a single JavaScript thread to execute the application code, which is the main thread. However, React Native also provides APIs that allow developers to create additional threads to offload work from the main thread and improve performance. These additional threads can be created using the Worker API or other third-party libraries.
It's important to note that creating too many threads can actually have a negative impact on the performance of the application, as each thread comes with its own overhead and can compete for resources with other threads. Therefore, it's important to use threads judiciously and only when necessary to improve the performance of specific tasks.
In React Native, a thread can refer to a separate execution context in the application that can run in parallel to the main thread. This can improve the performance and responsiveness of the application by allowing tasks to be performed in the background, without blocking the user interface.
One example of using threads in React Native is to perform time-consuming tasks, such as image processing or network requests, in a separate thread to prevent the UI from freezing or becoming unresponsive. Here is an example of using the Worker API to create a new thread for image processing:
import { Worker } from 'react-native-worker';
const worker = new Worker('path/to/worker.js');
worker.postMessage({ image: imageFile });
worker.onmessage = (event) => {
// Update UI with processed image data
};
worker.onerror = (error) => { console.log(error); };
In this example, we create a new Worker instance and pass it the path to a JavaScript file that contains the code for processing the image. We then send the image file to the worker using the postMessage method and handle the response using the onmessage callback.
Another example of using threads in React Native is to improve the performance of animations and other UI interactions by offloading work to a separate thread. Here is an example of using the Animated API to create a new thread for animating a component:
领英推荐
import { Animated } from 'react-native';
const position = new Animated.Value(0);
Animated.timing(position, {
toValue: 1, duration: 1000,
}).start();
In this example, we create a new Animated.Value instance and use it to animate the position of a component over a period of 1000 milliseconds. The Animated.timing method creates a new thread to handle the animation, which allows the main thread to continue rendering the UI without interruption. Once the animation is complete, the start method is called to update the UI with the new position of the component.
Developers can also use other third-party libraries, such as react-native-threads or react-native-multithreading, to create additional threads in their React Native applications.
Questions:
If thread can be closed then why it is harmful for the performance as if I use different threads while completing or changing the action and also closing it. then?
On what condition i use to create the threads?
Answers:
While it's true that threads can be closed or terminated, creating and managing multiple threads can still have a negative impact on the performance of the application. Here are a few reasons why:
Therefore, while using threads can improve the performance of specific tasks, it's important to use them judiciously and only when necessary to avoid the above issues. Developers should carefully consider the tradeoffs between using multiple threads and using a single thread before introducing additional threads into their application.
You should use threads in your React Native application only when it's necessary to improve the performance of specific tasks that are time-consuming or compute-intensive. Here are some conditions under which you may want to create threads:
It's important to note that creating too many threads can have a negative impact on the performance of the application, as each thread comes with its own overhead and can compete for resources with other threads. Therefore, it's important to use threads judiciously and only when necessary to improve the performance of specific tasks.