Step-by-step Provisioning of MySQL Heatwave Database in OCI | Create Compartment, VCN, Policy, Security List in Oracle Cloud
Introduction:
In this article, I will show you how to provision MySQL Heatwave database in Oracle Cloud. You will also learn-
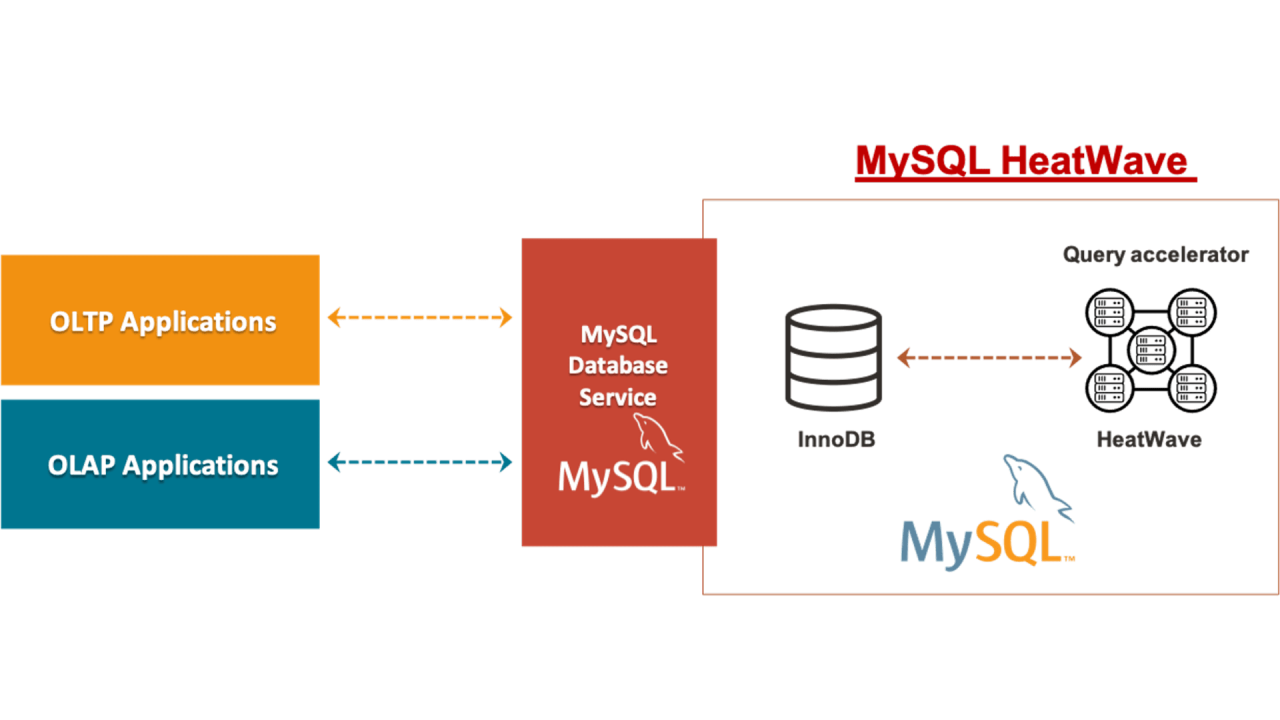
Before getting into it. Here is the quick brief of MySQL Heatwave-
MySQL HeatWave Database Service is a fully managed service, running on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. It enables you to:
Step 1: Create a Compartment
You must have an OCI tenancy subscribed to your home region and enough limits configured for your tenancy to create a MySQL HeatWave Database System. Make sure to log in to the Oracle Cloud Console as an Administrator. For testing, you can use oracle free tier account.
2. On the Compartments page, click Create Compartment.
3. In the Create Compartment dialog box, in the NAME field, enter MySQLHeatWave, and then enter a Description, select the Parent Compartment, and click Create Compartment.
Below screenshot shows a completed compartment.
Step 2: Create a policy for the compartment
2. On the Policies page, in the List Scope section, select the Compartment (root) and click Create Policy.
3. On the Create Policy page, in the Description field, enter MySQL_Services and select the root compartment.
4. Turn on the Show manual editor toggle switch in the Policy Builder section.
5. Click Create.
5. Enter the following required MySQL HeatWave policies. These policies define what actions the "Administrators" group can perform, with permissions ranging from inspecting compartments to fully managing MySQL database systems.
Allow group Administrators to {COMPARTMENT_INSPECT} in tenancy
Allow group Administrators to {VCN_READ, SUBNET_READ, SUBNET_ATTACH, SUBNET_DETACH} in tenancy
Allow group Administrators to manage mysql-family in tenancy
The following screenshot shows the completed policy creation:
3. Create a VCN
2. Click Start VCN Wizard.
3. Select VCN with Internet Connectivity and click Start VCN Wizard.
4. On the Create a VCN with Internet Connectivity page, in the Basic Information section, in the VCN Name field, enter HeatWave_VCN and from the Compartment drop-down list, select MySQLHeatWave.
5. Click Next at the bottom of the screen.
6. Review the Oracle Virtual Cloud Network (VCN), Subnets, and Gateways sections and click Create to create the VCN.
Note: The VCN creation is completed.
7. Click View Virtual Cloud Network to display the created VCN.
8. On the Virtual Cloud Network Details page, under Resources, select Security Lists (2).
Step 4: Configure security list to allow MySQL incoming connection HeatWave_VCNs
2. In the Security List for Private Subnet-HeatWave_VCN section, in the Ingress Rules section, click Add Ingress Rules.
3. In the Add Ingress Rule dialog box, add an ingress rule with Source CIDR 0.0.0.0/0 and destination port number 3306, 33060 and click Add Ingress Rule.
4. On the Security List for Private Subnet-HeatWave_VCN page, the new ingress rules will be shown in the Ingress Rules list.
Step 5: Create a MySQL HeatWave Database System.
2. Click Create MySQL HeatWave Database System.
3. Select the Development or Testing Option. Note: For your production deployment, Select the production one.
4. On the Create MySQL HeatWave Database System dialog box, complete the fields in each section:
Note: The New MySQL HeatWave Database System will be ready to use after a few minutes. The state will be shown as Creating during the creation.
Check the Status is Active Now.
Thanks for visiting. Subscribe and stay tuned.... :)
Mentions:
Database, Hadoop & Cloudera Administration
5 个月Great job.