Saving Keras Model
The Python3 command line is great to test out commands, and the ipython is the improvement on is as it provided a more interactive control. Jupyter Notebook is the web version derived from ipython.
This article is on saving a trained model to a file, and being able to retrieve it again in the Keras format. This assumes that the there is a working TensorFlow.
For a dataset, many models may be developed and proposed before one is agreed on. Saving it to disk allows a Data Engineer to manage and identify models that best suit the situation.
Step 1. Create the directory
[Ubuntu 24] Create the directory "models" to store the models files.
mkdir models
Step 2. Create the model and save the model as "my_model.keras"
[Ubuntu 24] Change to the python environment and start ipython, then enter the following codes
import tensorflow as tf
import os; os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '3'
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist; data = mnist.load_data(); type(data)
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
import numpy as py
matplotlib.use('tkagg')
num_classes = 10
input_shape = (28, 28, 1)
x_train = x_train / 255; x_test = x_test / 255
y_train = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes)
y_test = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, num_classes)
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential(
[
tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=input_shape),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(num_classes, activation="softmax"),
])
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
batch_size = 50
epoch = 10
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=batch_size, epochs=epoch, shuffle=True, validation_split=0.1)
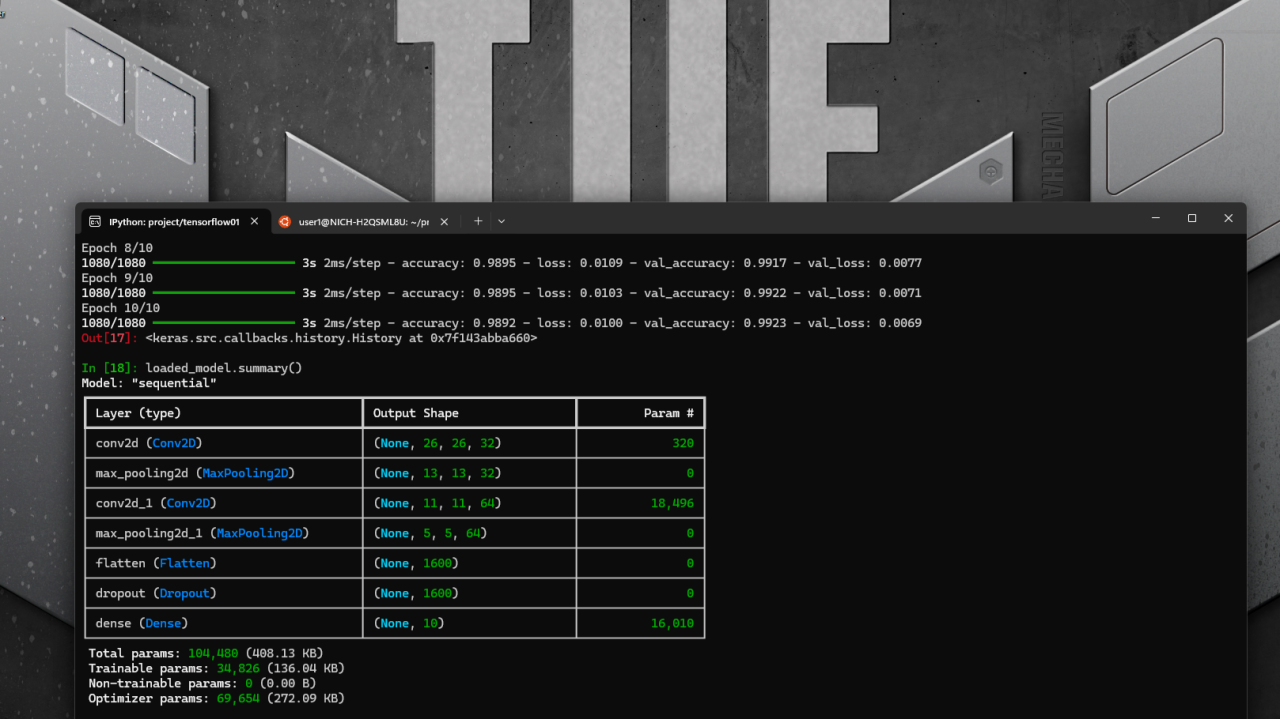
model.summary( )
The function summary( ) will show the model layers information. Here is an example to display the test result of this trained model.
scores = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=0)
print("%s: %.2f%%" % (model.metrics_names[1], scores[1]*100))
领英推è
Step 3. Save and load the trained model
This is saved in keras format. Open ipython and declare the imports as previously.
In ipython, to save the model
model.save('models/my_model.keras')
Load the trained model
new_model = tf.keras.models.load_model('models/conv2d_mnist_model.keras')
Step 4. Save and load model only
This is saved in json format. Open ipython and declare the imports as previously.
from tensorflow.keras.models import model_from_json
model_json = model.to_json()
with open("models/my_model.json", "w") as json_file:
json_file.write(model_json)
Load the model and train with provided data
json_file = open('models/my_model.json', 'r')
model_json = json_file.read()
json_file.close()
loaded_model = model_from_json(model_json)
loaded_model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
loaded_model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=batch_size, epochs=epoch, shuffle=True, validation_split=0.1)
Hopefully, you have found it useful to know how to save and load a Keras model to disk.