Persisting GeoSpatial Data in MongoDB
Persisting data is crucial in web applications, if data is not saved, the data is wiped out when a page refresh is done on the web browser, caching in the browser can be a way to mitigate the problem but that data still is temporary. Permanent storage is made possible by using a database or a text file or excel spreadsheet. A relational database management system is the way to go when you are serious about saving huge data over a long period of time.
When exploring database systems, you will come across in-memory, sql and no-sql databases. With SQL databases, data that is saved must conform to a specfic model that's created when designing the tables and that model resticts users from saving data fields that are not specified in that model, eg: When I do an insert into the names tables, that table has a name and password field but if I try to add additional data fields not in the model, the database will complain or restrict me from doing so. The data is saved in a tabular form.
NO-SQL database uses BSON, a format similiar to JSON format where data is saved as a key value pair and also has model implementation similar to SQL databases.
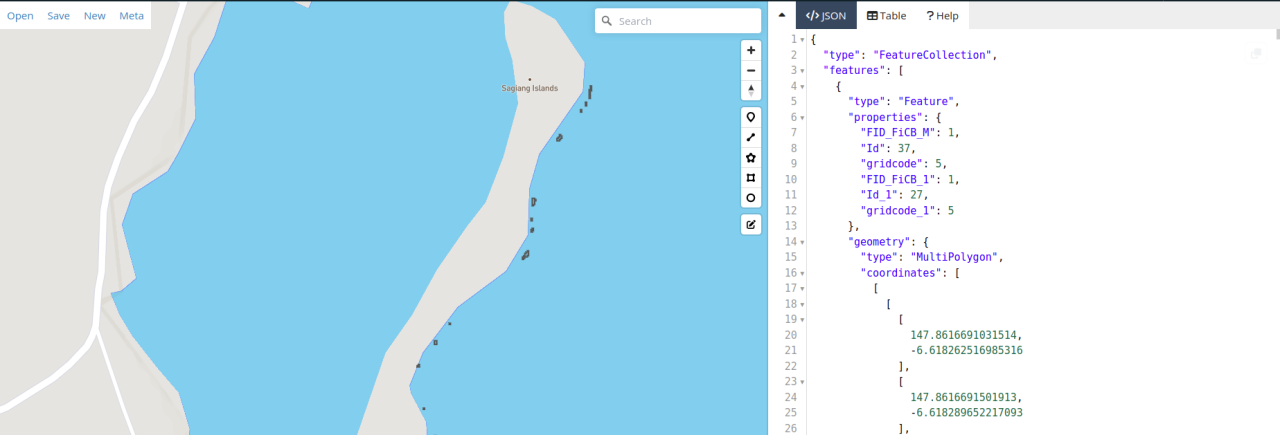
Our task was to save geospatial data in GEOJSON format into a mongo database, where data is uploaded from a user interface. We had to search the web for examples on how to model the geojson data in the below format. Below is a geojson multipolygon data.
{
?"type": "FeatureCollection",
?"features": [
??{
???"type": "Feature",
???"properties": {
????"Id": 37,
????"gridcode": 5
???},
???"geometry": {
????"type": "MultiPolygon",
????"coordinates": [
?????[[[
????????147.8616691031514,
????????-6.618262516985316
???????],?[
????????147.8616691501913,
????????-6.618289652217093
???????],?[
????????147.86169628700546,
????????-6.618289605179121
???????],??[
????????147.86169633404702,
????????-6.618316740410674
???????],??[
????????147.8616964751729,
????????-6.618398146105075
???????],[
????????147.86166933835275,
????????-6.618398193143824
???????],[
????????147.8616692913121,
????????-6.618371057912181
???????],??[
????????147.86164215449324,
????????-6.618371104949259
???????],[
????????147.86164196633848,
????????-6.618262564021611
???????],[
????????147.8616691031514,
????????-6.618262516985316
???????]]]]}},{
???"type": "Feature",
???"properties": {
????"Id": 37,
????"gridcode": 5,
???},
???"geometry": {
????"type": "MultiPolygon",
????"coordinates": [
?????[??[?[
????????147.86175098404107,
????????-6.618533728177976
???????],[
????????147.86175103108735,
????????-6.618560863408854
???????],?[
????????147.86177816791576,
????????-6.618560816364493
???????],[
????????147.8617782620119,
????????-6.618615086825756
???????],[
????????147.86180539884307,
????????-6.618615039779525
???????],?[
????????147.86180568114509,
????????-6.618777851161481
???????],?[
????????147.86175140746477,
????????-6.618777945254797
???????],[
????????147.86175131336924,
领英推荐
????????-6.618723674793502
???????],?[
????????147.8617241765317,
????????-6.61872372183755
???????],[
????????147.86172408243993,
????????-6.61866945137573
???????],?[
????????147.86172403539433,
????????-6.618642316144777
???????],[
????????147.86169689856106,
????????-6.61864236318676
???????],[
????????147.8616968044734,
????????-6.618588092724355
???????],?[
????????147.86172394130372,
????????-6.618588045682761
???????],[
????????147.86172389425872,
????????-6.618560910451735
???????],?[
????????147.8617238472139,
????????-6.61853377522066
???????],[
????????147.86175098404107,
????????-6.618533728177976
???????]??]]]}}
An this is what we ended up with enabling us to save a multipolygon geojson file into the database and querying to from the user interface.
const geometrySchema = new mongoose.Schema({
type: {
type: String,
enum: ['Polygon'],
required: false
},
coordinates: {
type: [[[Number]]],
index:'2dsphere',
required: false
}
});
const propertiesSchema=new mongoose.Schema({
type:String,
Id: {
type: String,
required:false
},
gridcode:{
type:String
}
})
const featureObjectSchema=new mongoose.Schema({
type:{
type:String,
enum:['Feature'],
default:'Feature'
},
properties:{type:propertiesSchema},
geometry:{type:geometrySchema}
})
const CoralSchema = mongoose.Schema({
createdAt: {
type: Date,
default: Date.now
},
name:{
type:String
},
type:{
type:String,
enum:['FeatureCollection'],
default:'FeatureCollection'
},
features:{
type:{}
}
});
Entries in the mongo Database replicating the the geojson format above.