OSPF Protocol
Mourad A. HARIMA
Telco Cloud, 5G Engineer @LabLabee | 5GaaS | OpenRAN | AWS | SDN | NFV | Bash Scripting
cost = 10^8/BW.?
OSPF is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) designed for use within an autonomous system (AS), which is a collection of networks under a single administrative domain.??
- Administrative distance (AD) of 110
- Uses Dijkstra's Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm to determinate the best path for a remote network.
OSPFv2 : Used for IPv4?
OSPFv3 : Used for IPv6
- Routers exchange information about their interfaces (directly connected networks) so that each router builds a map of the entire network topology.
- OSPF uses Link state Advertisement (LSA) and Link State Database (LSDB) for building the map.
?
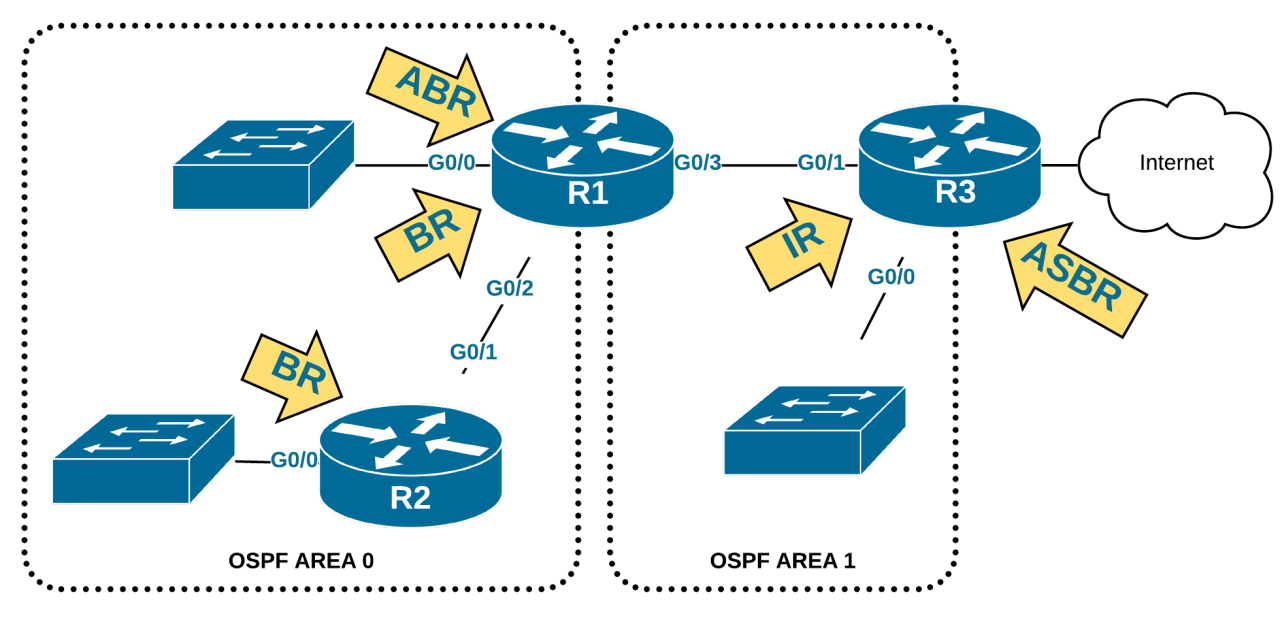
?- OSPF supports a hierarchical design "Areas" to break a large network with one large LSDB into smaller areas with smaller separate LSDBs.
- Areas is a group of links and routers that share the same LSDB
- Areas should be contiguous.
-All not backbone areas must connect to the backbone area by having at least one ABR.
- Interface in the same subnet must be in the same area
- Has a LSDB for each area?
- Creates summary informations about each subnet in an area to advertise it into other areas, "Summary LSA"
- It is recommended to connect ABR with two areas only (backbone and other area).
- Enabling OSPF on an interface means that router will start sending and receiving hello packets out of the interface to discover neighbors and establish adjacencies with them.
Hello packets are always sent to the multicast IP address 224.0.0.5.
- Hello interval/timer : how often a router sends hello messages (default 10 sec)
- Dead interval/timer : how long a router waits without received a hello message from a neighbor before believing that neighbor has failed (default 4x hello timer)
OSPF Network Types : Configuration that are implemented on each OSPF-enabled interface
Two types of the OSPF network types : MBA and Point-to-Point
1- Broadcast (MBA) : network type is configured by default on ethernet interfaces?
-Broadcast network type tells the router to dynamically discover OSPF neighbors
-A Designated Router (DR) and backup Designated Router (BDR) must be elected on each subnet to reduce the amount of ospf traffic on multiaccess networks.
- A DR manages the LSDB exchange process :
- only DR and BDR form full adjacency with other OSPF routers.
-The DR/BDR is responsible for updating the LSDBs of all other OSPF routers using the multicast IP address 224.0.0.5 (all OSPF routers)
- When an LSA changes on DROthers, they send an LSU (LSA update) packet to 224.0.0.6 (all DRs/BDRs)
-When a DR fails, the BDR will operate as a DR.
-The DR/BDR election :?
1. The highest OSPF interface priority (Default priority is 11,(0-255))
2. The router with the highest RID
- The first election is for the DR, and the second one is for the BDR.
2- OSPF Point-to-point : network type exists for serial links that use PPP or HDLC as layer two encapsulation
-Like Broadcast network type, Point-to-Point network type tells the router to dynamically discover OSPF neighbors
-Serial links do not have the ability to add a third router to the link, so there is no DR/BDR election.
-Routers establish full adjacency.
Telecom and IP Network Engineer | Final Year Student at Yahia Fares University | ISC2 Member | Cisco Certified | Juniper Certified | Fortinet Certified
1 年Thank you for sharing such Precious informations with us
Cybersecurity Engineer | Aspiring Cybersecurity Professional
1 年Very informative and straight to the point. Great post ??