Microfluidics-Assisted Nanoprecipitation Shows Promise for Theranostic Applications
PreciGenome
LifeScience & Microfluidics (Lipip Nanoparticle Synthesis, PCR Machine& Kit, Single-Cell&Droplet, Cell Perfusion, etc.)
Breakthrough in Nanocarrier Technology: Microfluidics-Assisted Nanoprecipitation Shows Promise for Theranostic Applications
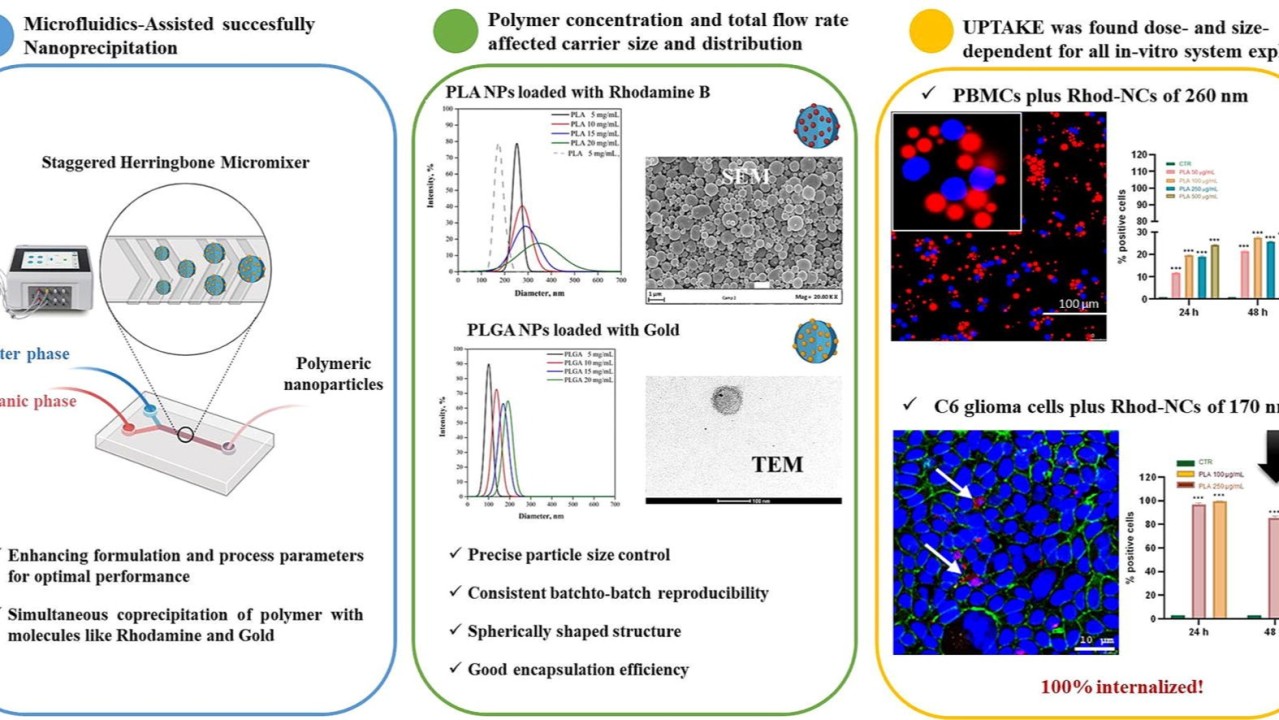
A recent study published in the International Journal of Pharmaceutics has demonstrated significant advancements in the fabrication of nanocarriers using microfluidics-assisted nanoprecipitation. This innovative technique shows great potential for developing theranostic nanodevices, which combine diagnostic and therapeutic functions in a single platform.
Key Findings:
Dr. G. Della Porta, the study's lead researcher, commented, "This microfluidics-assisted approach offers unprecedented control over nanocarrier fabrication, enabling the development of more sophisticated theranostic platforms with potential applications in personalized medicine and advanced therapeutic strategies."
The study utilized a comprehensive suite of instruments, including the NanoGenerator Flex microfluidic system for nanoparticle synthesis, and advanced electron microscopy techniques to characterize the nanocarriers thoroughly.
This research represents a significant step forward in the field of nanomedicine, potentially paving the way for more effective and personalized treatments for various diseases. The ability to precisely control nanocarrier properties and incorporate both diagnostic and therapeutic elements could revolutionize drug delivery and medical imaging techniques. As the field progresses, further studies will likely focus on optimizing these nanocarriers for specific medical applications and advancing them towards clinical trials.