Mastering the Art of Application Lifecycle Management: A Comprehensive Guide
Proeffico Solutions Private Ltd.
We offer AI consulting services and custom products to help businesses understand how technology can help them scale.
In the current dynamic digital environment, software applications are essential for corporate performance, making application lifecycle management (ALM) a crucial practice. By streamlining an application's entire lifecycle—from its inception to its eventual retirement—this all-encompassing strategy guarantees peak performance, efficacy, and alignment with corporate objectives.
Dissecting Application Lifecycle Management: What It Really Is
In order to manage each stage of an application's lifecycle, ALM is fundamentally an integrated system that synchronises people, procedures, and resources. It acts as a framework that provides direction, allowing companies to create, test, implement, and manage software applications quickly and accurately. ALM increases productivity, improves product quality, and makes related product and service administration and maintenance easier by coordinating the many components of an application's life cycle.
The Strong Argument in Favour of Adopting ALM
ALM becomes a potentally in a time when software updates are released on a daily basis and companies are trying to obtain a competitive advantage. It speeds up processes, guaranteeing that high-caliber products get to market quickly, and encourages cooperation between teams from different departments, such as development, operations, and security. Additionally, ALM gives organisations the ability to establish and adhere to suitable requirements, implement strict testing procedures, and dynamically modify development processes over the course of the software life cycle.
The Adaptive Phases of the Asset LifeCycle
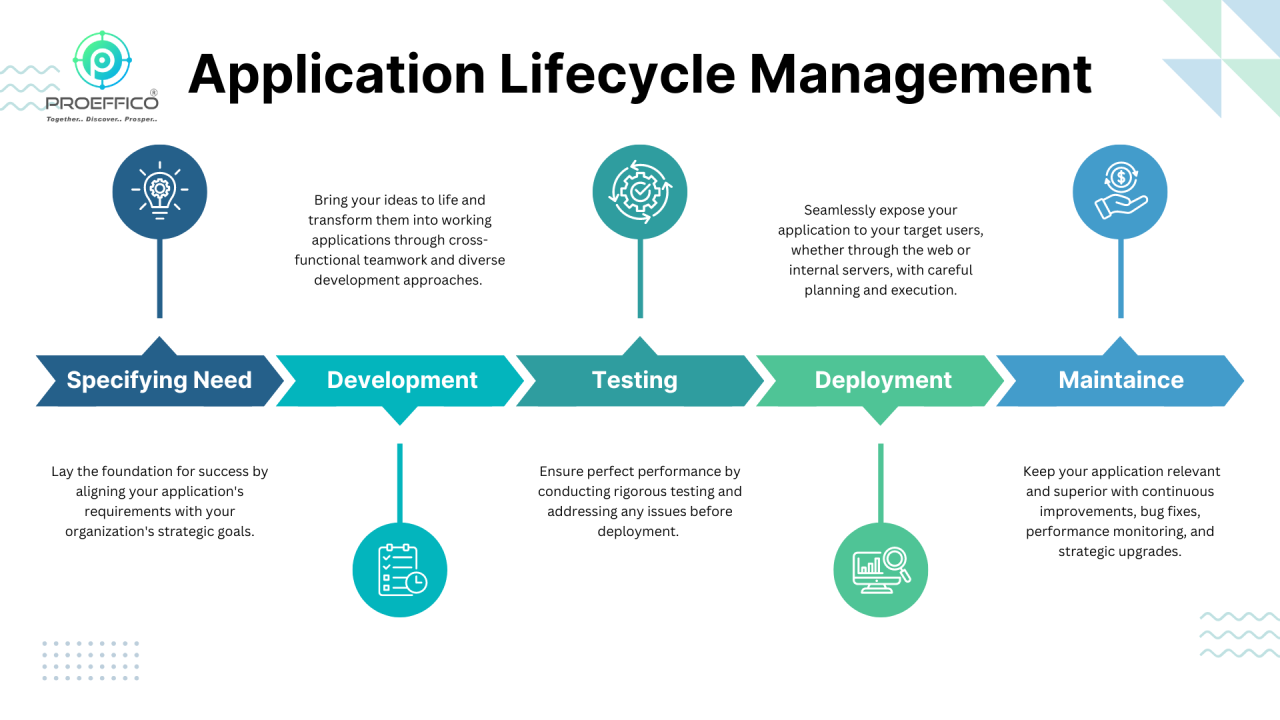
Each of the five unique steps that make up the ALM process is a comprehensive journey that is essential to the effective delivery and maintenance of software applications.
1. Specifying Needs: The Basis for Achievement
Stakeholders from different disciplines come together in this first phase to express their requirements and goals for the application. Based on these stated needs, a thorough design is created. These criteria can include everything from usability and performance concerns to corporate objectives and regulatory requirements. In order to guarantee that the application is in line with the organization's strategic goals, this step establishes the foundation for the following stages.
2. Development: Giving Concepts Life
The development process starts once requirements are established and turns concepts into real, working applications. Creating a development strategy, dividing the requirements into digestible parts, and utilising different approaches—like the iterative Agile approach or the sequential Waterfall model—are all part of this step. During this stage, cross-functional teamwork is essential to ensuring that the developed product satisfies all requirements and is simple to use, test, and implement.
3. Testing and Quality Control: Guaranteeing Perfect Performance
Since testers provide test environments, test cases, and ongoing input during the development process, testing and quality assurance frequently coincide with the development stage. Testers confirm that the application satisfies stakeholder expectations, complies with specified criteria, and goes through extensive functional and integration testing during the formal testing process. The development team rapidly addresses any issues or faults found, guaranteeing the stability and quality of the product before delivery.
4. Deployment: Exposing the App to the Public
The application is made available to its target users at the deployment stage. The procedure differs according to the kind of programme; web applications can be accessed through the internet, while software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications are installed on internal servers. This phase requires careful preparation and execution to guarantee a smooth transfer from development to production.
5. Ongoing Upkeep and Enhancement: Maintaining Superiority
The journey doesn't end with deployment; ongoing upkeep and enhancement are crucial to guarantee the longevity and applicability of the programme. In this phase, the team works to fix any defects that are still present, keeps an eye on performance, and plans upgrades and improvements in response to user input and changing business requirements. This phase also entails defining the retirement strategy for the system and figuring out when to switch to a newer version or a completely different product.
Enjoying the Benefits of Successful ALM Implementation
Embracing application lifecycle management can help organisations realize a multitude of benefits that add real value to their operations.
领英推荐
By encouraging openness and cooperation amongst teams, ALM makes it possible to track requirements, strategies, changes, and project status in real time. Stakeholders are better equipped to make decisions and match software goals with more general organisational objectives thanks to this increased visibility.
2. Increased Observance and Management
Throughout the life cycle of an application, organisations may use ALM to create strong governance frameworks and guarantee adherence to internal standards and industry laws. By being proactive, you may reduce risks and protect against expensive infractions or security breaches.
3. Quicker Time to Market
?ALM facilitates quicker deployments by optimising workflows and automating procedures, enabling businesses to quickly adapt to changing market conditions and seize new possibilities. This flexibility gives you a competitive edge in the fast-paced business world of today.
4. Improved Quality of the Product
Applications are guaranteed to satisfy the highest standards of functionality, performance, usability, and security because of ALM's emphasis on thorough testing, continuous integration, and quality assurance procedures. As a result, businesses are able to produce excellent goods that satisfy consumers and enhance their reputation.
Providing Sturdy Tool Suites to Boost ALM
Organisations use a set of specialised tools that integrate people and processes throughout the application life cycle to fully realise the potential of application life management. Version control, real-time team planning and communication, requirements, test, source code, automated deployment, and application portfolio management are just a few of the capabilities that these technologies have to offer.
ALM tool alternatives that are popular include, but are not limited to, Tuleap, Microsoft Azure DevOps, Visure, Codebeamer, Jama Software, and MeisterTask, Jira. Organisations should give top priority to aspects that meet their unique requirements when choosing an ALM product, such as scalability, integration capabilities, and user-friendliness.
Getting Around the ALM Landscape: Best Practices and Things to Think About
Organisations should use the following best practices to enable the successful implementation of ALM and to optimise its benefits:
Conclusion
Application life cycle management is a powerful paradigm that empowers organisations to create high-quality software applications effectively and efficiently in the constantly changing digital context. Businesses may promote cooperation, improve compliance, shorten time-to-market, and produce better, customer-focused goods by adopting ALM.
When companies start their ALM journey, they should thoroughly evaluate their particular requirements, choose the right tools, and put best practices into practice that are customised for their particular objectives. In an increasingly software-driven world, companies may gain a competitive edge, spur innovation, and succeed over the long term with a well-executed ALM strategy.
At Proeffico, we offer comprehensive ALM solutions that can transform your application development and management. Contact us today to experience the power of ALM and propel your organization to new heights.