Laravel Applications with Request Context
The request context refers to any data or information specific to a single HTTP request. This data can include details about the current user, the request payload, IP address, headers, or even custom information that you want to pass along during the request lifecycle.
By storing and managing this data effectively, you can:
Setting Up Request Context
Step 1: Create a Custom Middleware
php artisan make:middleware ApiRequestLogger
After creating the middleware, modify as follows
<?php
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Closure;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Log;
use Illuminate\Support\Str;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Context;
class ApiRequestLogger
{
/**
* Handle an incoming request.
*
* @param \Closure(\Illuminate\Http\Request): (\Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response) $next
*/
public function handle(Request $request, Closure $next): Response
{
Context::add('request_id', Str::uuid()->toString());
Context::add('request_path', $request->path());
Context::add('request_method', $request->method());
Context::add('payload', $request->all());
$startTime = microtime(true);
$response = $next($request);
$endTime = microtime(true);
$executionTime = $endTime - $startTime;
$responseTime = number_format($executionTime * 1000);
Context::add('response_time', $responseTime);
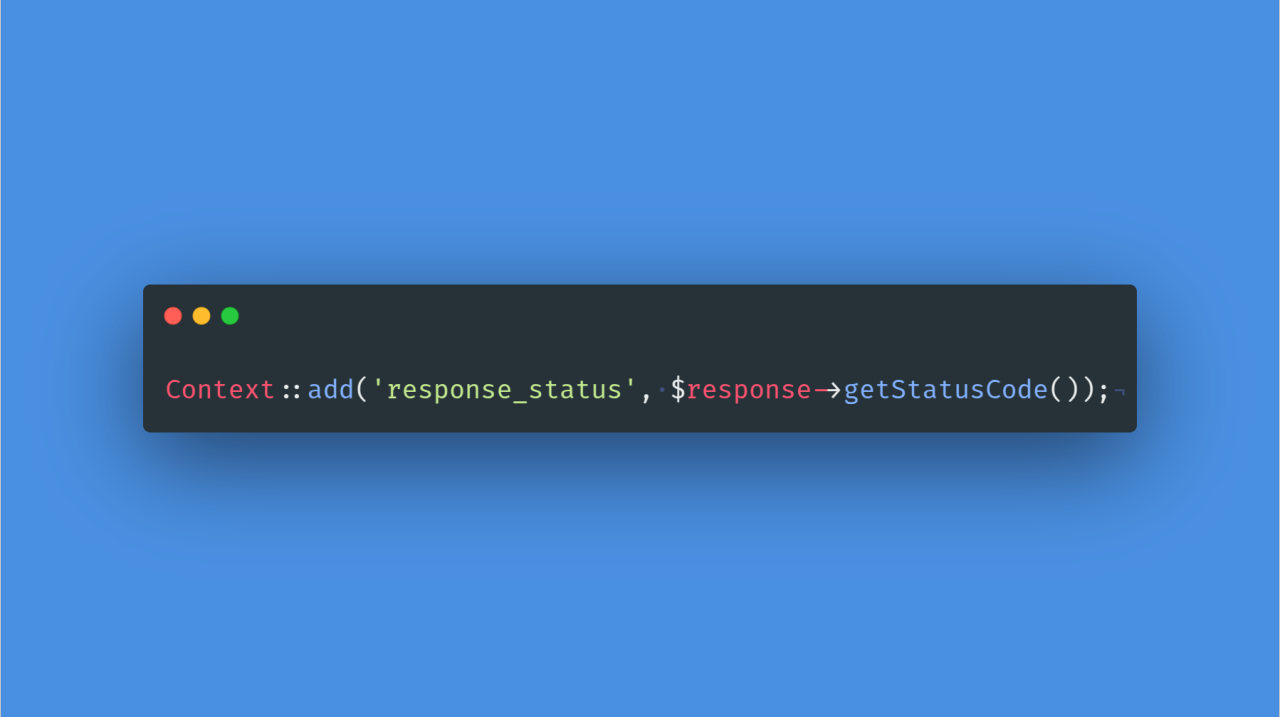
Context::add('response_status', $response->getStatusCode());
Log::info('API Request processed');
return $response;
}
}
Step 2: Register the Middleware
<?php
use Illuminate\Foundation\Application;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Configuration\Exceptions;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Configuration\Middleware;
return Application::configure(basePath: dirname(__DIR__))
->withRouting(
web: __DIR__.'/../routes/web.php',
api: __DIR__.'/../routes/api.php',
commands: __DIR__.'/../routes/console.php',
health: '/up',
)
->withMiddleware(function (Middleware $middleware) {
$middleware->append([
\App\Http\Middleware\ApiRequestLogger::class,
]);
})
->withExceptions(function (Exceptions $exceptions) {
//
})->create();
Register the middleware in bootstrap/app.php
领英推荐
Step 3: Call an API
I'm using Postman here
Step 4: Validating log
Now we can validate the context of the request by checking the logs storage/logs/laravel.log
As you can see the complete details of the request including how much time it took to respond (in seconds).
Conclusion
Request context is a simple yet powerful concept that can significantly improve how you handle request-specific data in Laravel. By centralizing this data, you can streamline logging, debugging, and application behavior, ultimately leading to cleaner and more maintainable code.
Try implementing request context management in your Laravel projects and see how it can make your application development process smoother and more efficient.
To learn more about Laravel Context, please visit Laravel's official website