Indexing and Hashing in DBMS
Huzaifa Asif
Engineering Lead | Solution Architect | Cloud Engineer | FinTech | SaaS | PaaS | AWS | Azure | GCP
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of data management, efficient access and retrieval of information lie at the heart of a well-designed database system. Two powerful techniques, Indexing and Hashing, have emerged as key players in optimizing database performance. We will discuss Indexing and Hashing, exploring their unique strengths, use cases, and why they are essential components for any high-performance database.
Section 1: Indexing in DBMS
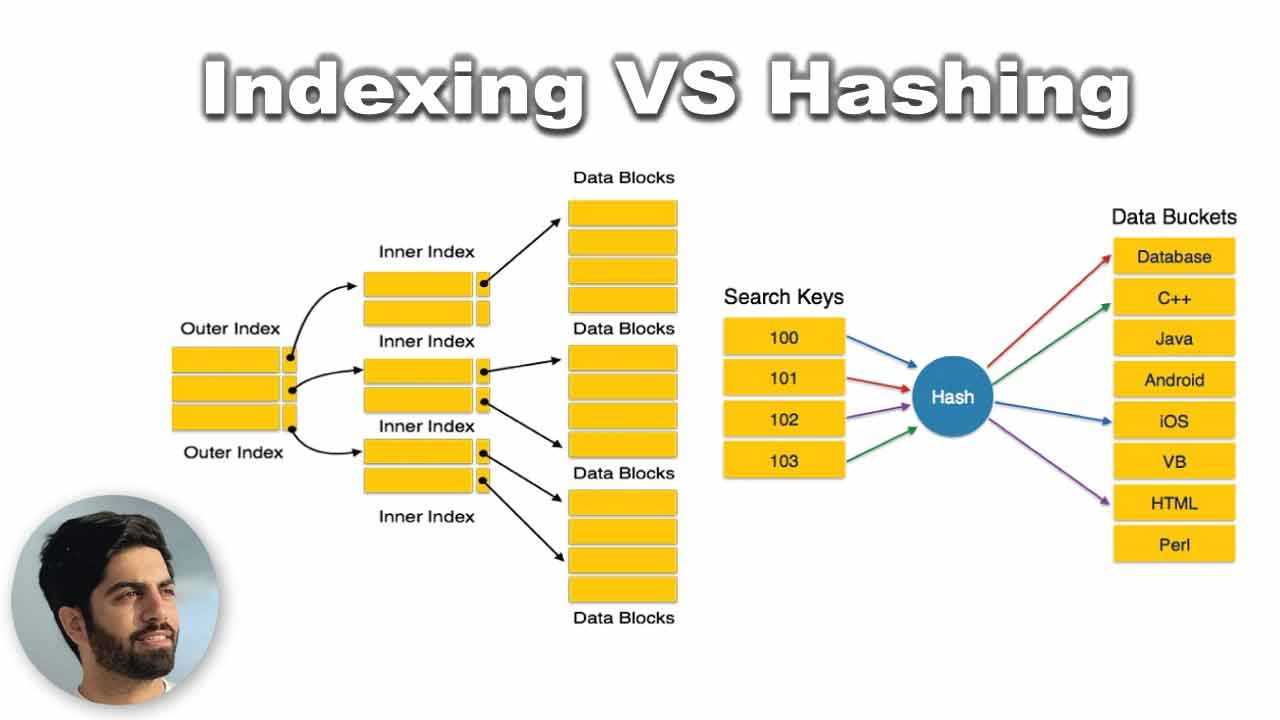
Indexing serves as a gateway to rapid data retrieval in a database. Its primary objective is to reduce the number of disk accesses required when processing queries, making it a valuable asset for improving database performance. How does it work?
When an index is created for a particular field in a database table, it generates a specialized data structure that holds the field value alongside a pointer to its corresponding record. These indexes can be developed using one or more columns from the table, enabling rapid access to data without the need for time-consuming full table scans.
Types of Indexing
Section 2: Hashing in DBMS
Hashing revolves around using mathematical functions, known as hash functions, to calculate direct locations of data records on a disk. But how is it different from Indexing, and why is it an invaluable asset for specific database tasks?
Unlike Indexing, Hashing doesn’t rely on index structures to access data. Instead, it generates unique addresses for data records using hash functions, which take search keys as parameters. This direct calculation of data locations on the disk allows for faster retrieval, making Hashing an ideal choice for large databases.
Types of Hashing:
Section 3: Indexing vs Hashing
Each technique, Indexing, and Hashing, possesses its unique strengths that cater to different use cases in the database world. Let’s compare them against each other.
Data Retrieval Speed
Storage Efficiency
Database Size
Complexity
Section 4: Indexing Use Cases and Best Practices
As we’ve seen, both Indexing and Hashing have their time and place in the database landscape. Let’s explore some real-world use cases and best practices to harness their full potential
Indexing Use Cases
Best Practices:
Section 5: Hashing Use Cases and Best Practices
Hashing, with its unique approach to data retrieval, offers distinct advantages in specific scenarios:
Hashing Use Cases
Best Practices:
Conclusion
Indexing and Hashing play crucial roles in database management, offering unique advantages to cater to different scenarios. Indexing proves invaluable in optimizing small to medium-sized databases, while Hashing shines in larger databases where rapid data retrieval and storage efficiency are paramount.
As database architect or developer, understanding the strengths and best practices of Indexing and Hashing empowers us to design high-performance systems that efficiently manage and retrieve vast amounts of information. By leveraging the power of these two techniques, we can unlock the full potential of our databases and provide seamless and rapid access to data for our users and applications.