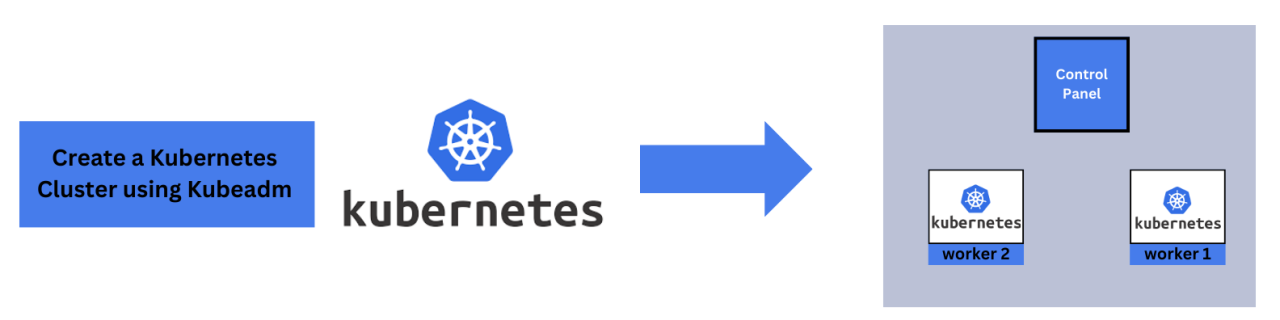
Guide to Setting Up a Kubernetes Cluster on CentOS
Muhammad Shaheer
Microsoft Certified DevOps Engineer | Azure Admin | Terraform Certified
Are you looking to set up a Kubernetes cluster for your applications but unsure where to start? Kubernetes, an open-source container orchestration platform, can help manage and scale your containerized applications with ease. In this guide, we'll walk you through the step-by-step process of setting up a Kubernetes cluster on CentOS, using Kubernetes version 1.27.
Prerequisites
Before we dive into the installation process, ensure that you have the following prerequisites:
Step 1: Installing a Runtime
Remove the Older Version of the Docker
sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
Set Up the Docker Repository
sudo yum install -y yum-utils
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
Install Containerd
sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
Step 2: Install and Configure Prerequisites
sudo tee /etc/modules-load.d/k8s.conf <<EOF
overlay
br_netfilter
EOF
sudo modprobe overlay
sudo modprobe br_netfilter
sudo tee /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf <<EOF
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
EOF
sudo sysctl --system
Verify sysctl Configuration
sysctl net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables
sysctl net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables
sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward
Step 3: Configuring the systemd cgroup driver
Edit the Containerd Configuration
sudo tee -a /etc/containerd/config.toml <<EOF
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc.options]
SystemdCgroup = true
EOF
sudo systemctl restart containerd
Step 4: Install Kubeadm, Kubelet, and Kubectl
领英推荐
Set SELinux to Permissive Mode
sudo setenforce 0
sudo sed -i 's/^SELINUX=enforcing$/SELINUX=permissive/' /etc/selinux/config
Add the Kubernetes yum Repository
sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo <<EOF
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
exclude=kubelet kubeadm kubectl cri-tools kubernetes-cni
EOF
sudo yum install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl --disableexcludes=kubernetes
sudo systemctl enable --now kubelet
Step 5: Initialize the Control Plane
Make sure Containerd is running
sudo systemctl status containerd
Initialize the control plane
kubeadm init
Step 6: Post-Initialization Setup
After the control plane has been initialized successfully, run these commands
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Step 7: Join the nodes
Use the join token to join the worker nodes to the cluster.
kubeadm join <control-plane-host>
Step 8: Install the Pod Network
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/weaveworks/weave/releases/download/v2.8.1/weave-daemonset-k8s.yaml
Change the Configuration Options
kubectl get ds -A
kubectl edit ds weavenet
Under the environment variable section, add:
- name: IPALLOC_RANGE
value: 10.244.0.0/16