GitLab CI/CD: Automating Your DevOps Workflow
BABATUNDE GANIYU
DevOps Engineer | Flutter Developer | Database Administrator | Software Engineer | ChatBot Developer | Site Reliability Engineer | Cloud Computing Developer
In today’s fast-paced development environment, continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) have become the backbone of efficient software development. GitLab CI/CD, integrated directly into the GitLab platform, offers a robust solution to automate testing, building, and deployment processes, ensuring that your code is always production-ready.
What is GitLab CI/CD?
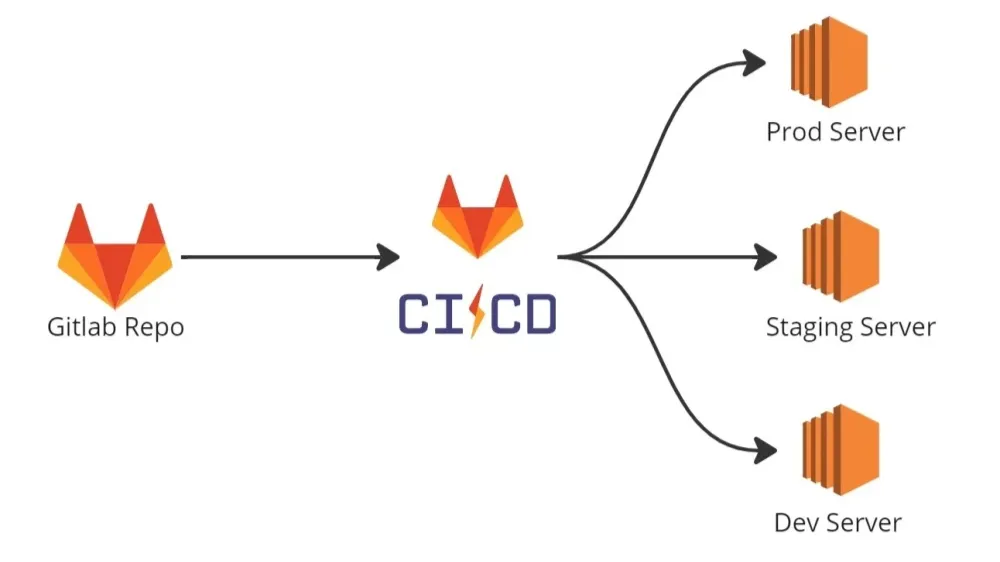
GitLab CI/CD is a set of built-in features within GitLab that enable developers to automate the entire software development lifecycle—from code commit to deployment. By using a simple configuration file (.gitlab-ci.yml), teams can define a series of jobs that will run automatically in a specified order. This integration allows for a seamless workflow, reducing manual intervention and streamlining the path to production.
Key Features and Benefits
1. Integrated Platform
GitLab CI/CD is built into the GitLab ecosystem, eliminating the need for separate tools for version control and CI/CD. This integration means that all your code, issue tracking, code reviews, and CI/CD pipelines are housed in one platform, simplifying management and improving collaboration.
2. Flexible Pipeline Configuration
Using a YAML-based configuration file (.gitlab-ci.yml), developers can define:
3. Powerful Runners
GitLab Runners are lightweight agents that execute the jobs defined in your pipelines. They can be self-hosted or provided by GitLab, offering flexibility in terms of performance, scalability, and security. Custom runners can be tailored to your environment, ensuring that your CI/CD process fits your unique needs.
4. Enhanced Visibility and Reporting
GitLab CI/CD provides detailed logs and reports for each job, making it easier to diagnose issues and understand the performance of your pipelines. The visual pipeline editor helps teams see the flow of the CI/CD process at a glance, improving transparency and collaboration.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Whether you’re a startup or an enterprise, GitLab CI/CD scales with your needs. You can run pipelines concurrently across multiple runners and distribute workloads to optimize speed and resource utilization.
领英推荐
How GitLab CI/CD Works
Pipeline Definition
At the heart of GitLab CI/CD is the .gitlab-ci.yml file. This file resides in the root directory of your repository and outlines the entire pipeline process. Here’s a simplified example:
stages:
- build
- test
- deploy
build_job:
stage: build
script:
- npm install
- npm run build
artifacts:
paths:
- dist/
test_job:
stage: test
script:
- npm test
deploy_job:
stage: deploy
script:
- ./deploy.sh
environment:
name: production
url: https://your-app.example.com
In this example:
Runners in Action
Once you push your code, GitLab CI/CD triggers the pipeline and schedules the jobs to run on available runners. Runners can be configured to run jobs in Docker containers, virtual machines, or even on bare metal, providing a flexible execution environment that can mimic your production setup.
Auto DevOps
For teams that want to streamline their CI/CD process even further, GitLab’s Auto DevOps feature can automatically detect your project’s language and configuration, setting up pipelines with sensible defaults. This is particularly useful for smaller teams or projects looking to get started quickly with CI/CD without extensive manual configuration.
Best Practices for Using GitLab CI/CD
Furthermore, GitLab CI/CD is a powerful tool that transforms how teams build, test, and deploy applications. Its seamless integration into the GitLab ecosystem, flexible pipeline configuration, and scalable runner options make it a top choice for modern DevOps practices. By automating your workflow with GitLab CI/CD, you can accelerate delivery cycles, improve code quality, and ultimately, bring your software to market faster.
Whether you’re a seasoned DevOps professional or just starting with CI/CD, GitLab CI/CD offers the tools and flexibility needed to streamline your development process and keep your team focused on what truly matters—building great software.
Do share your thoughts or experiences with GitLab CI/CD in the comments. Happy coding!