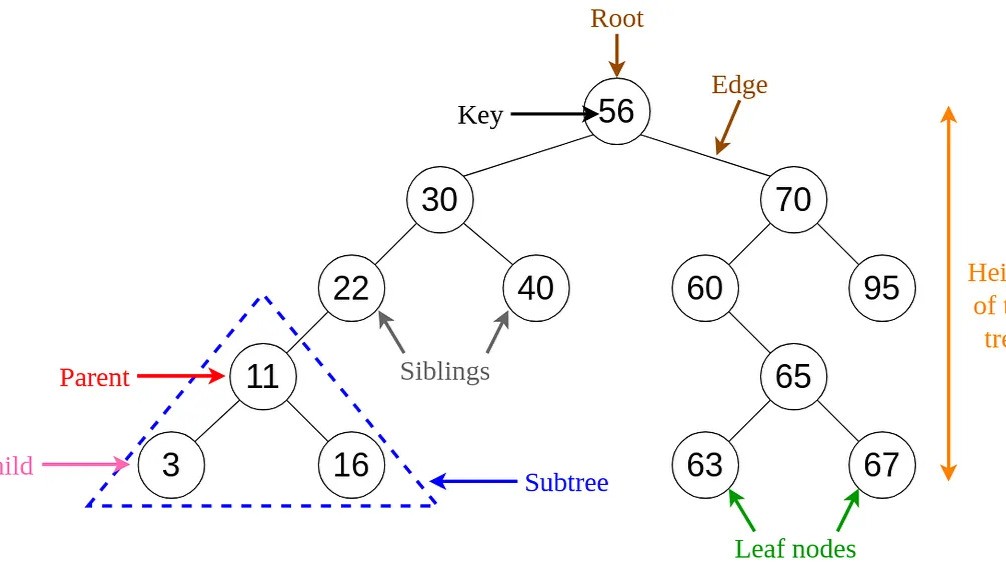
The Binary Search Tree (BST)
In the realm of computer science and software engineering, efficient data management is critical to performance, especially when dealing with large-scale data sets. One fundamental data structure that plays a key role in this is the Binary Search Tree (BST). Its sorted structure and optimal time complexity for key operations make it a go-to choice for many real-world applications. In this article, we’ll explore what a BST is, its properties, and how it can be leveraged for efficient searching, insertion, and deletion.
What is a Binary Search Tree (BST)?
A Binary Search Tree is a binary tree that maintains a specific ordering of nodes, making it highly efficient for search operations. Each node contains the following properties:
This inherent ordering is what allows a BST to efficiently search, insert, and delete nodes.
Example of a BST:
15
/ \
10 20
/ \ / \
5 12 18 25
In this example, for every node, the left child contains values smaller than the node, and the right child contains values larger than the node. For the root node 15, all nodes in the left subtree (10, 5, 12) are smaller, and those in the right subtree (20, 18, 25) are larger.
Key Operations in a BST
Balanced vs. Unbalanced BST
A balanced BST ensures that the height of the tree is kept at a minimum, typically O(log n), ensuring that all operations (search, insert, delete) maintain optimal efficiency. However, an unbalanced BST (one that behaves like a linked list) can degrade these operations to O(n) time complexity.
To prevent such degradation, self-balancing trees like AVL Trees or Red-Black Trees automatically maintain balance after insertions or deletions, ensuring the tree remains efficient.
Applications of Binary Search Trees
BSTs are incredibly versatile and form the foundation of several real-world applications:
领英推荐
Advantages of Using a BST
When to Use BSTs
BSTs are highly efficient for problems where:
However, if you're dealing with frequently accessed data or need guaranteed balance, consider using a self-balancing BST like an AVL tree or Red-Black tree to avoid performance degradation over time.
Conclusion
The Binary Search Tree is a fundamental data structure that provides efficient search, insertion, and deletion operations for dynamically changing datasets. Understanding the basic properties and operations of BSTs opens the door to more advanced data structures and algorithms that can further optimize performance in real-world applications.
Whether you are developing databases, search engines, or file systems, mastering BSTs and their variants will significantly enhance your problem-solving abilities and enable you to build efficient, scalable systems.
About the Author:
Shakil Khan,
Pursuing BSc. in Programming and Data Science,
IIT Madras.